PowerTransformer#
The PowerTransformer() applies power or exponential transformations to numerical
variables.
Let’s load the house prices dataset and separate it into train and test sets (more details about the dataset here).
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from feature_engine import transformation as vt
# Load dataset
data = data = pd.read_csv('houseprice.csv')
# Separate into train and test sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
data.drop(['Id', 'SalePrice'], axis=1),
data['SalePrice'], test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
Now we want to apply the square root to 2 variables in the dataframe:
# set up the variable transformer
tf = vt.PowerTransformer(variables = ['LotArea', 'GrLivArea'], exp=0.5)
# fit the transformer
tf.fit(X_train)
The transformer does not learn any parameters. So we can go ahead and transform the variables:
# transform the data
train_t= tf.transform(X_train)
test_t= tf.transform(X_test)
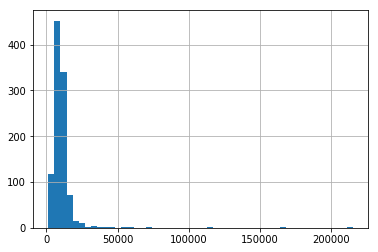
Finally, we can plot the original variable distribution:
# un-transformed variable
X_train['LotArea'].hist(bins=50)
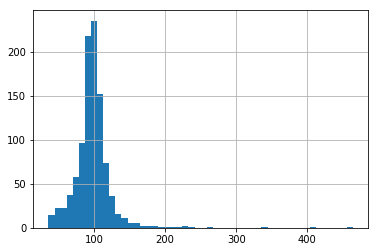
And now the distribution after the transformation:
# transformed variable
train_t['LotArea'].hist(bins=50)
Additional resources#
You can find more details about the PowerTransformer() here:
For more details about this and other feature engineering methods check out these resources:

Feature Engineering for Machine Learning#
Or read our book:

Python Feature Engineering Cookbook#
Both our book and course are suitable for beginners and more advanced data scientists alike. By purchasing them you are supporting Sole, the main developer of Feature-engine.
